Kalidas Subedi.
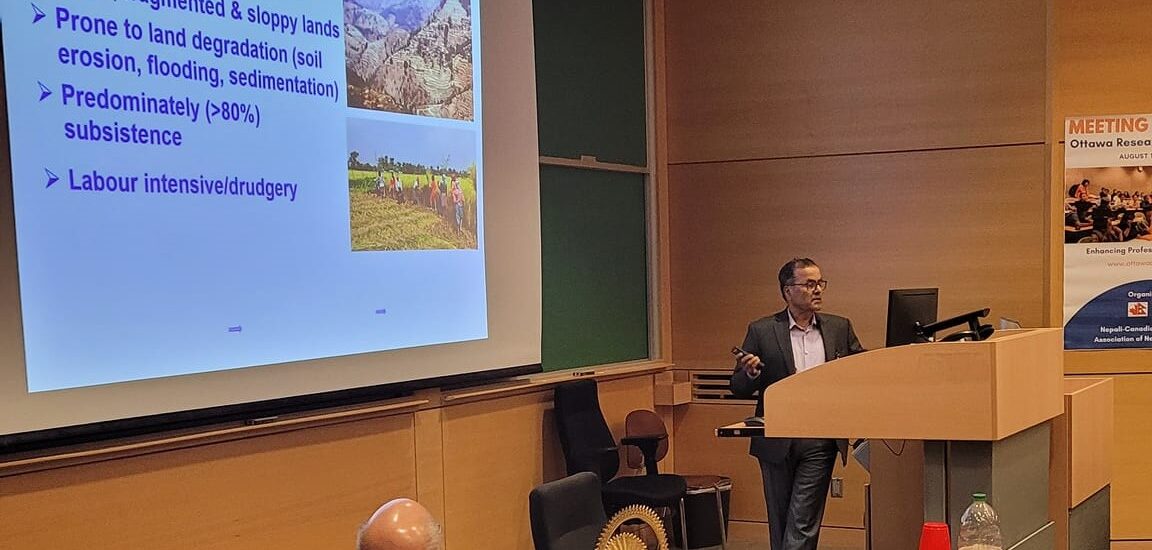
Agriculture is considered as the backbone of Nepalese economy and livelihood. Still, agricultural production and productivity are low and far behind to meet the country’s food requirements. There is an ever-increasing trend of food import leading to a huge trade deficit and food security concerns. Nepal has a tremendous agroecological potentials and natural resources to produce ample foods for its domestic consumption, but its potentials are not fully utilized. The traditional agricultural practices are subsistence in nature, characterized by small land holdings, rainfed production systems and sloppy landscapes that are highly prone to degradation. Although some progress has been made in agriculture development, they are not up to the level of investment. In this paper, the potentials, underlying challenges, crop yield gaps and ways how Nepal can increase and sustain its agricultural productivity through different transformative approaches are discussed. The natural potentials including gifted climatic conditions, irrigation potentials, diverse production niches and market opportunities are discussed. Similarly, current challenges of loss of agricultural lands, soil degradation, land fragmentation, inputs supply systems and labour shortages are highlighted. Some practical approaches of sustainable land management and production boosting measures are outlined. Protection and consolidation of agricultural lands, investment on irrigation, plant nutrients supply and crop genetic improvement, niche-based cash crops production along with value addition and assured markets are the suggested key focus areas.
View/Download the presentation from here.
Keywords: Nepal, agriculture, production constraints, land management, food security
Author: Kalidas Subedi, PhD